Hbv Dna Iuml Normal Range
Electronic Health Informatics Data To Describe Clearance Dynamics Of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Hbsag And E Antigen Hbeag In Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Mbio

Association Of Hepatitis B E Antigen And Dna Viral Load With Severity Of Liver Dysfunction And In Hospital Outcomes In Hepatitis B Related Liver Cirrhosis Hou Ame Medical Journal

Viral Hepatit Dergisi

Hbv Dna Level Of Each Rflp Elisa Hbv Genotyped Group Log Iu Ml Download Table
Www Agajournals Org Article S1542 3565 16 1 Pdf
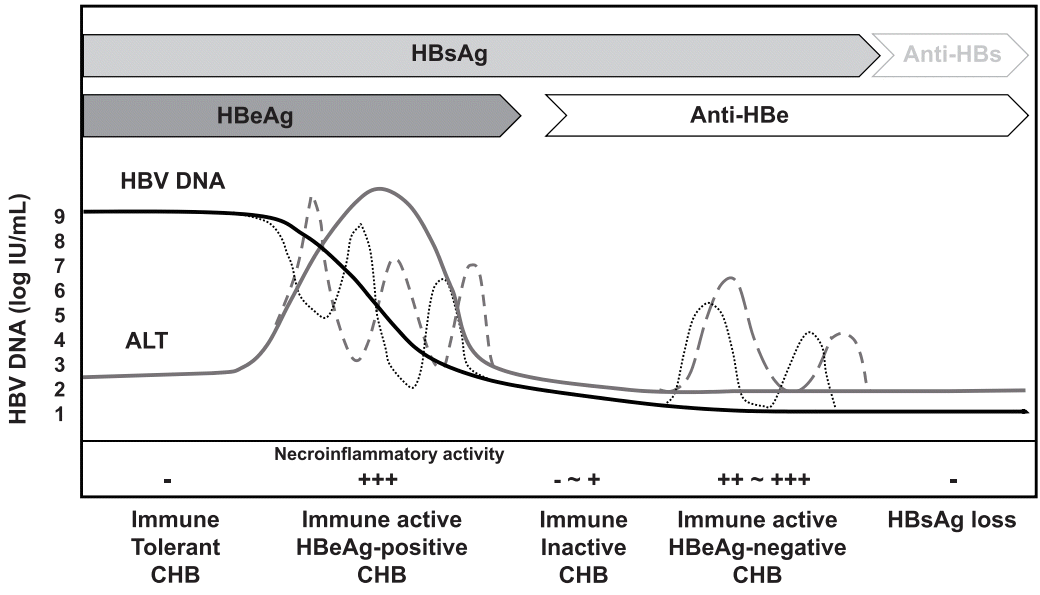
Kasl Clinical Practice Guidelines For Management Of Chronic Hepatitis B
Normal range for this assay is Not Detected.
Hbv dna iuml normal range. Inactive carriers refer to HBeAg-negative individuals who have normal serum ALT levels and low (<. It is noteworthy that untreated patients with an intermediate serum HBV DNA level (,000–1,000,000 IU/mL) among the untreated pEDNA group, despite the normal ALT level, are paradoxically more likely to develop HCC than are untreated patients with a high serum HBV DNA level (>1,000,000 IU/mL). Value Flag Reference Range HEPATITIS B DNA QNT PCT 4.0 H < 1.6 log IU **** Viral load result for HBV DNA is 9,450 IU/ML*** 1 IU/ML is 5 copies/mL.
No therapy was initiated since aminotransferases had returned to normal range. The percentage of participants with HBV DNA < IU/mL at Week 48 was analyzed, which included participants who have the last available on-treatment HBV DNA, IU/mL in the Week 48 analysis window. Lft normal, HBV DNA 13 iu/ml and HBsAG (eliza test) austrailian antigen comes 1.36 ( decreasing per yr) in how long can I be relieved of hepatitis b?.
Normal range Normal ALT level ALT level between 1 to 2 times the upper limit of normal range Positive HBe antigen Order HBVQN / Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Detection and Quantification by Real-Time PCR, Serum Order serum ALT level Negative HBe antigen Normal ALT level and HBV DNA <2,000 IU/mL Normal ALT level Elevated ALT level Monitor ALT annually. The method used for HBV DNA Viral Load PCR is COBAS TaqMan HBV Test. The median serum HBV DNA and HBV RNA was 7745 (4710–36 380) IU/mL and 154 (44.6–977) U/mL, respectively.
An “Undetected” result indicates that hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA was not detected in the specimen. If quantitative results are desired, the original specimen should be diluted with HBV-negative human plasma or serum depending upon the matrix of the original specimen, and the test repeated. Patients were excluded with coexistent HDV, HCV, human immunodeficiency virus, or active cytomegalovirus infection or with evidence of cirrhosis or other liver disease.
This assay cannot accurately quantify HBV DNA below this. The quantification range of this assay is 10 to 1,000,000,000 IU/mL (1.00 log to 9.00 log IU/mL). Robert Rahimi answered 8 years experience in Hepatology.
Only one study gave data on ALT, in which 21-40 IU/L in comparison with below IU/L was a significant independent predictor;. All non-normal distribution data were presented as the median and interquartile range and normal distribution data were presented as mean±SD. The quantitative range of this assay is 1.00-9.00 log IU/mL (10-1,000,000,000 IU/mL).
Inactive Carrier - ≤00 IU/ml ≤ULN Monitor a or liver biopsy stage 1 -3 and/or grade 1 3;. Persons with chronic HBV infection can either be inactive carriers or develop chronic hepatitis. Serum HBV DNA concentrations can vary from undetectable to more than 10 9 IU/mL during the course of chronic HBV infection.
Below the threshold, the viral load is considered “undetectable” – something everyone with chronic hepatitis B wants to hear. Measurements per year and one HBV DNA measurement per year. The 48-week cumulative rate of HBV DNA >00 IU/mL was 58.1%.
Is milky discharge from nipples a symptom of normal 03 wk. The sensitivity of HBV DNA tests may vary with each lab so it’s a good idea to use the same lab for your test. 25.2 ± 8.3 IU/L, p = 0.031) levels differed significantly between true inactive carriers and false inactive carriers (Table1).
Hbeag negative and HBV DNA quantification results 36 iu/ml liv function test are normal range any treatment available?. An "Undetected" result indicates that hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA was not detected in the serum specimen. The result is expressed in international units per millilitre (IU/mL), with each unit representing approximately 6 viral particles per millilitre of blood.
The evidence was of low quality. A study of 3653 carriers from Taiwan concludes that an HBV DNA level of at least 104 copies/mL (≥00 IU/mL) is a strong risk predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma (14). Delivering on clinical need requirements Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA detection and viral load measurement are essential for treatment decisions and patient monitoring.
The genotype assay is only triggered when the quantitative test result is ≥500 IU/mL. 1 log = 10 copies. Univariate and multivariate analysis of factors at treatment cessation associated with HBV DNA >00 IU/mL are depicted in table 2.
Results into copies/mL or IU/mL. Than 100,000 copies/mL, it may be written HBV DNA > 5 log copies/mL or 105 copies/mL. An interpretation of "Not Detected" does not rule out the presence of inhibitors in the patient specimen or HBV DNA concentration below the level of detection of the test.
Interpretation The quantification range of this assay is 10 to 1,000,000,000 IU/mL (1.00 log to 9.00 log IU/mL). After resumption of NUCs, patients were followed up every 8 to 16 weeks. End-of-treatment serum HBV RNA and off-treatment serial HBV RNA were both independently associated with HBV DNA >00 IU/mL (HR 2.959, 95% CI 1.776 to 4.926, p<0.001;.
The detectable range with this method is 6 - 110,000,000 IU/ml (35 - 640,0,000 copies/ml). Values of HBV DNA above thresholds ranging from 5 log10 copies/ml (,000 IU/ml) to 2.9 log10 copies/ml (40 IU/ml) were significant independent predictors. URN ALT (ALT ≥ 30U/L for males or ≥ 19U/L for females) and LRN ALT (ALT < 30U/L for males or <19U/L for females), according to the guidelines of the American.
At this visit, HBV-DNA was 23.0 IU/mL. I just got my result on hbv viral load and is 40 iu/ml hbv dna load is 233cp/ml. The patients were subcategorized into two subgroups:.
Not detected A specimen with a result of "Not Detected" cannot be presumed to be negative for HBV DNA. My question is what does the 4.0 stand for?. The National Institutes of Health have suggested that viral loads that exceed 100,000 copies/mL be.
An "Undetected" result indicates that hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA was not detected in the serum specimen. Thirty-seven patients (59.7%) had HBV RNA ≥44.6 IU/mL. Not applicable Summary of Treatment Candidate Selection Based on Clinical Stage, HBeAg, HBV DNA and Serum ALT.
813 ± 570 IU/mL, p < 0.001) and ALT (22.2 ± 8.6 IU/L vs. 1 IU is equivalent to about 5 HBV DNA copies depending on the assay. What does this mean.
Main inclusion criteria were as follows:. They should be considered inactive carriers as long as ALT levels stay normal and HBV DNA levels are within the 2,000 to ,000 IU/mL range (Fig. Most HBV DNA assays in use are real-time PCR assays with a limit of detection of 10– IU/mL and a linear range of detection up to 10 9 IU/mL.
– 170,000,000 IU/mL (1.3 - 9.2 Log IU/mL) 1 IU/mL of HBV DNA is approximately 5. copies/mL A negative result (“Not Detected”) does not rule out the presence of HBV below the limit of detection of the assay or the presence of inhibitory substances. Lower Sensitivity of assay is 10 HBV DNA IU/mL. Patients with chronic liver disease of unknown origin most commonly have HBV that is detected by viral DNA testing.
A change from 10 to 100 is a 1-log increase;. There was no case with persistently normal ALT and HBV DNA levels higher than ,000 IU/mL. Hepatitis B Virus DNA, Quantitative, Real-Time PCR - Chronic carriers will persist in producing detectable HBV.
Number of Participants With HBV DNA by PCR >= 50 IU/mL Through Week 72 Time Frame:. Every log rise or fall is equivalent to a ten-fold increase or decrease. The method of determining percentage of participants with HBV DNA levels < IU/mL (target detected/not detected i.e., lower limit of detection) at.
The quantitative test has a range of 10 IU/mL to 1,000,000,000 IU/mL. HR 2.278, 95%. Compared with patients with HBV DNA of 00 IU/mL or less, the relative risk of cirrhosis was 2·5 (95% CI 1·6–3·8) and of hepatocellular carcinoma was 2·7 (1·3–5·6) in patients with serum HBV DNA of more than 00 IU/mL.
A “Detected” result with the comment, “HBV DNA level is < IU/mL (<1.30 log IU/mL). The HBV DNA levels ranged from 4.14 to 10.94 (in log 10 IU/mL), while the HBsAg level ranged from 2.08 to 5.38 (in log 10 IU/mL). Serum HBV DNA was quantified using the Determination Kit for hepatitis B viral DNA (Sansure Biotech, China), with a detection range of 1×10 2 to 5×10 8 IU/mL.
Sions and any level of detectable HBV DNA, whereas an inactive chronic HBV carrier state was considered to be present in 35 patients with persistently normal ALT and HBV DNA levels between 2,000 and ,000 IU/mL. HBV infection in all participants at baseline was HBeAg-negative/anti-HBe positive with HBsAg ≥1000 IU/mL, HBV DNA >00 IU/mL and ALT <10 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). HBV DNA => 50 IU/mL = approximately => 300 copies/mL.
Rebound of HBV DNA was defined as having detectable serum HBV DNA of ≥100 IU/ml, which was equivalent to a ≥1 log increase from undetectable levels. Antiviral therapy (i.e., lamivudine, telbivudine, and tenofovir) has been studied as an intervention to reduce perinatal HBV transmission among pregnant women with high HBV DNA levels (e.g., average HBV DNA levels of 7.6 log10 IU/mL) (144). NUCs were recommenced when HBV DNA levels further rose to ≥2,000 IU/ml (3.3 log IU/ml).
In HBV DNA viral load estimation, what is the equivalent of IU/ml = log10 IU/ml or log10 copies/ml?. Is it the same as 9,450 IU/ML?. The evidence quality was moderate.
10 - 1,000,000,000 HBV DNA IU/mL or 1.00-9.00 log10 IU/ml Normal range:. Therefore, NAs are recommended in this group during the last trimester of pregnancy to achieve low viraemia levels at delivery 17. The quantification rand of this assay is to 170,000,000 IU/mL (1.30-8.23 log IU/mL).
A positive HBV-DNA level (greater than 115 copies of the virus per mL > IU/mL) indicates that the virus is multiplying in the individual’s body and the person is contagious. 1 cobas ® HBV for use on the cobas ® 4800/6800/00 Systems provides security in your results with primers and probes targeting the highly conserved pre-core and core regions of the HBV genome. Hepatitis B DNA Viral Load PCR Blood Test measures the amount of Hepatitis B viral load or Hepatitis B virus DNA (HBV DNA) levels in the blood of chronically infected patients.
1.3 - 8.2 IU/mL (-170,000,000 IU/mL non-log transformed values) Positive results less than IU/mL will be reported as "POS 1.3 LOG IU" and negative results will be reported as "Not detected". After knowing the normal range of hepatitis b surface antibody, you should take a test to check whether you have Hepatitis B or not. The Mean ± SD baseline HBV DNA level (248 ± 385 IU/mL vs.
Patients between 18 and 65 years of age with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positivity for more than 6 months, HBV DNA levels >,000 IU/ml for hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)–positive patients or >00 IU/ml for HBeAg-negative patients, and consent for liver biopsy before receiving antiviral therapy. Second, HBeAg‐positive mothers with normal ALT but high serum HBV DNA levels (>10 6–7 IU/ml) have >10% risk of vertical HBV transmission to the newborn despite HBV immunoglobulin and vaccination. Results 114 entecavir-treated patients (median age 58.4 years, median serum HBsAg 54.4 IU/mL) with median treatment duration of 6.7 years were recruited.
Upper limit of normal. HBV viral loads detected at less than IU/mL are not quantitated. Analytical range in log10 values:.
Horizontal dotted line indicates ALT>50 IU/ml and vertical dotted line indicates HBV DNA> 000 IU/ml. The quantification range of this assay is 15 to 100,000,000 IU/mL (1.18 log to 8.00 log IU/mL) Except for immunocompromised patients or patients with suspected acute hepatitis, laboratory evaluation of hepatitis C (HCV) infection status should begin with HCV serologic testing, including testing for the presence of HCV antibodies. Inactive Chronic HBV Infection HBeAg-negative patients with PNALT (ALT every 3-4 months for 1 year) and HBV DNA <2,000 IU/mL repre-.
The researchers found that the risk of liver cancer was positively associated with increasing levels of HBV DNA and HBsAg in dose-response manners.The adjusted odds ratios ORs increased from 2.11 (95% CI, 0.99 to 4.5) to 10.47 (95% CI, 5.06 to 21.68) for those with HBV DNA level of 00-19,999 IU/ml or ≥,000 IU/ml compared with subjects with HBV DNA <00 IU/ml. Report results as “greater than 1.10E+08 HBV DNA IU/mL”. Calculated IU/mL are above the range of the assay.
B ALT normal range is based on local laboratory reference range;. If the test results show high Hepatitis B viral load levels than normal range and signs of liver damage it may indicate that you are at an active stage of Hepatitis. Labs usually measure down to less than 0 IU/mL.
So i have 47,250 copies/mL?. Chronic hepatitis B was defined as follows:. Here, the test itself consists of antibody tests and antigen tests.
The antigen test, will start exposing the result which before the symptoms appear. Still facing an unclear episode of hepatitis one month earlier, less common causes of acute hepatitis were examined. The quantification is homogeneous for all HBV genotypes tested.
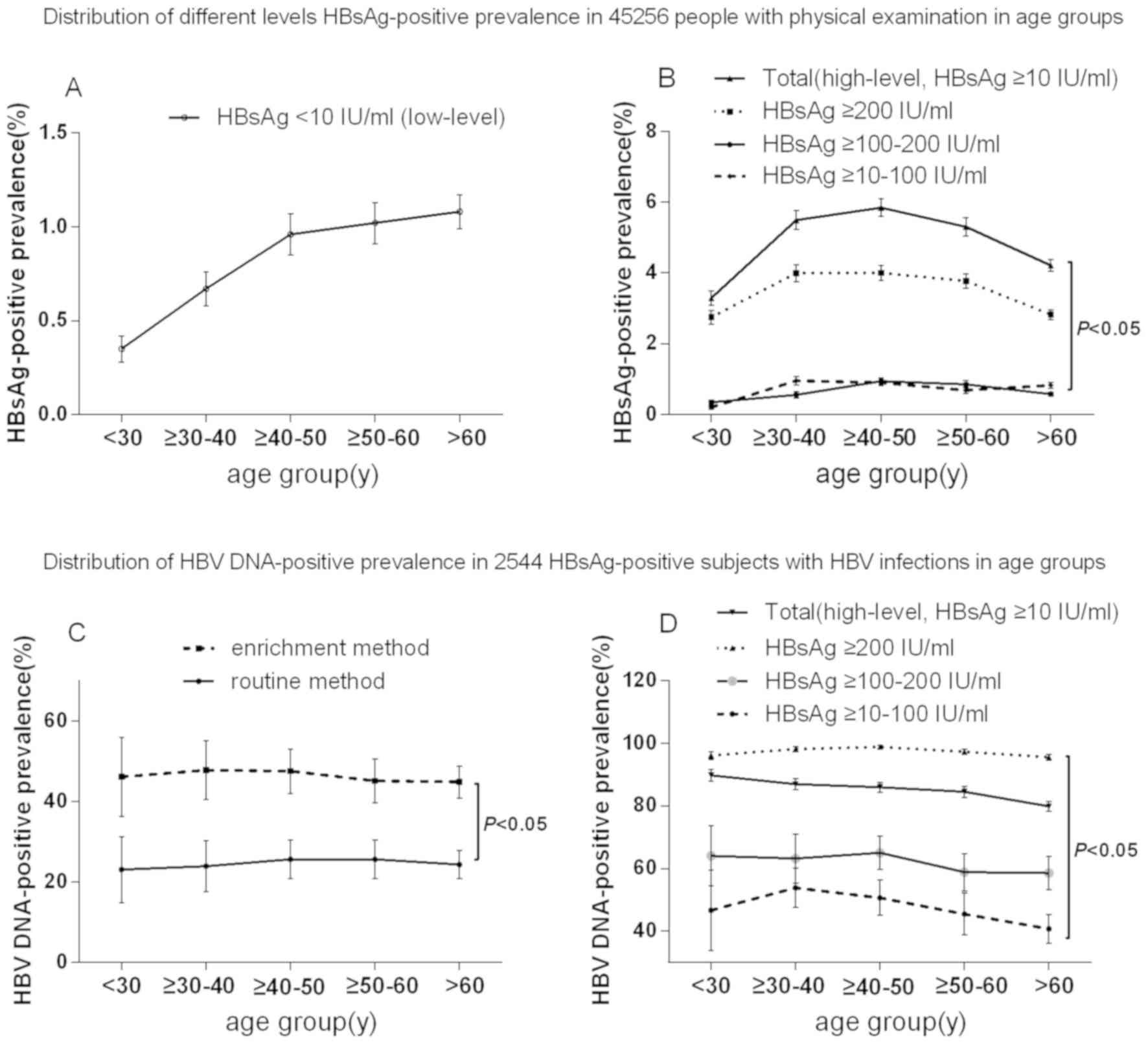
Clinical Characteristics And Association Analysis Of Persistent Low Level Hbsag Expression In A Physical Examination Population With Hbv Infection

Association Between Negative Results From Tests For Hbv Dna And Rna And Durability Of Response After Discontinuation Of Nucles T Ide Analogue Therapy Sciencedirect

A Real Time Quantitative Assay For Hepatitis B Dna Virus Hbv Developed To Detect All Hbv Genotypes
View Of A Genotype Specific Baseline Score Predicts Post Treatment Response To Peginterferon Alfa 2a In Hepatitis B E Antigen Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Annals Of Gastroenterology

Serum Hepatitis B Virus Dna Rna And Hbsag Which Correlated Better With Intrahepatic Covalently Closed Circular Dna Before And After Nucleos T Ide Analogue Treatment Journal Of Clinical Microbiology

Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B An Update And Prospect For Cure Intechopen

Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Quantification Why And How To Use It In 11 A Core Group Report Sciencedirect

Baseline Serum Hepatitis B Virus Hbv Dna Levels In 150 Patients With Download Scientific Diagram
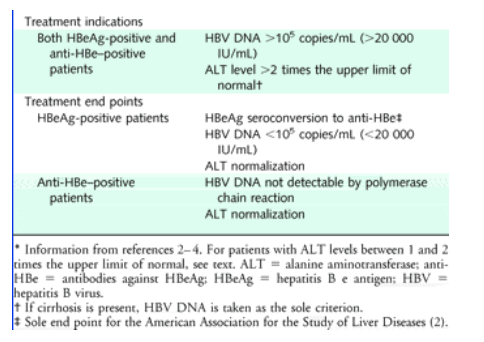
The Natural History And Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B A Critical Evaluation Of Standard Treatment Criteria And End Points Hbv Dna Alt
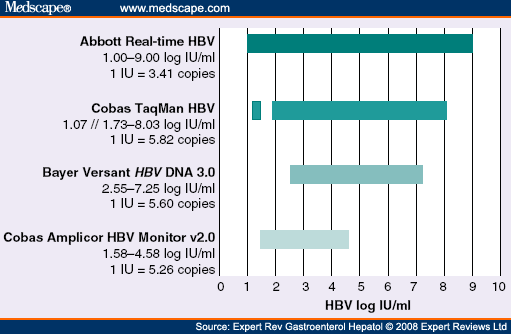
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B Virus Infection

Characterization Of Hbeag Negative Chronic Hepatitis B In Western Brazilian Amazonia
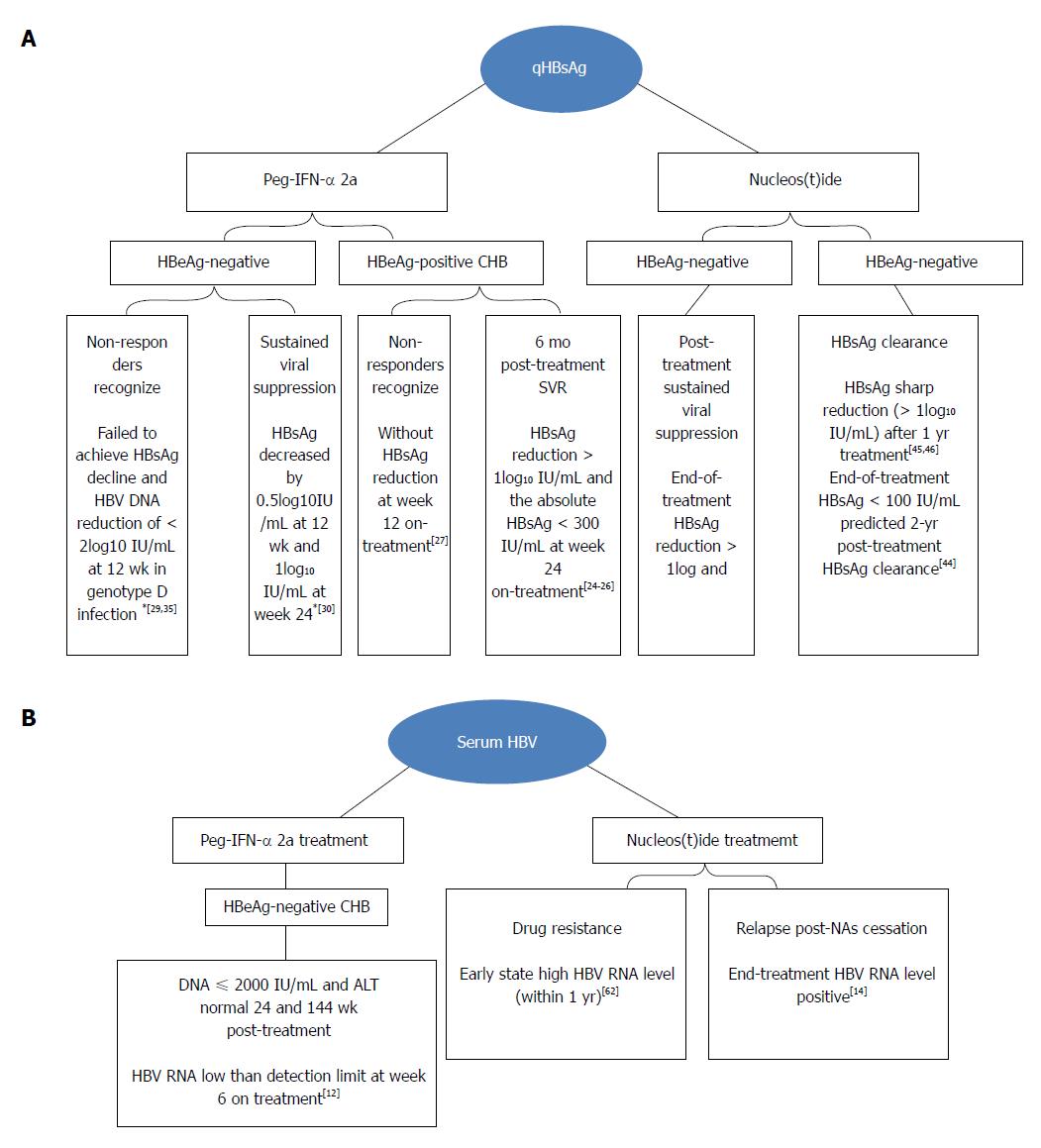
Progression And Status Of Antiviral Monitoring In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B From Hbsag To Hbv Rna
View Of A Genotype Specific Baseline Score Predicts Post Treatment Response To Peginterferon Alfa 2a In Hepatitis B E Antigen Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Annals Of Gastroenterology
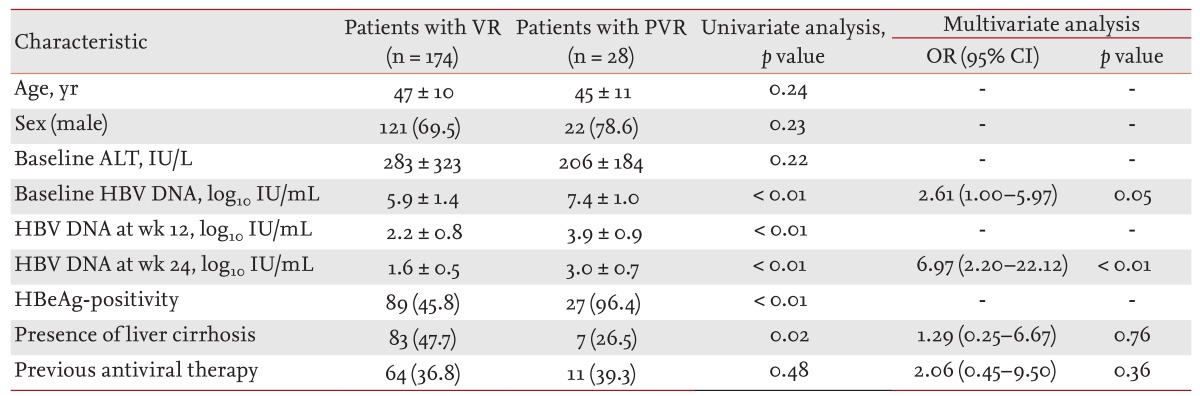
Long Term Virological Outcome In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With A Partial Virological Response To Entecavir
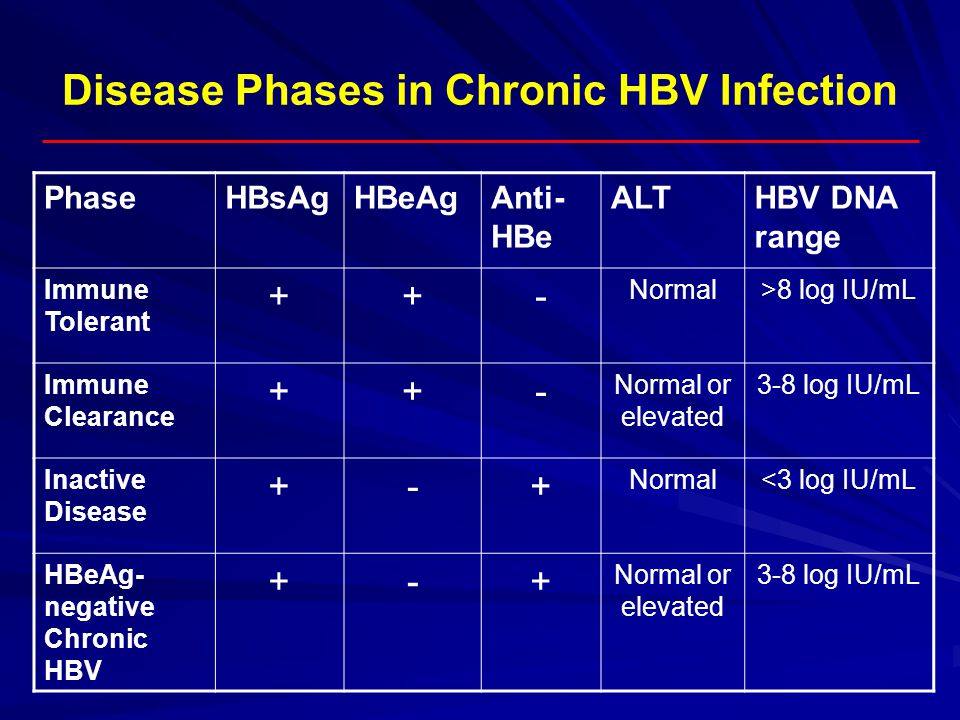
Laboratory Diagnostics In Hepatitis Ppt Video Online Download
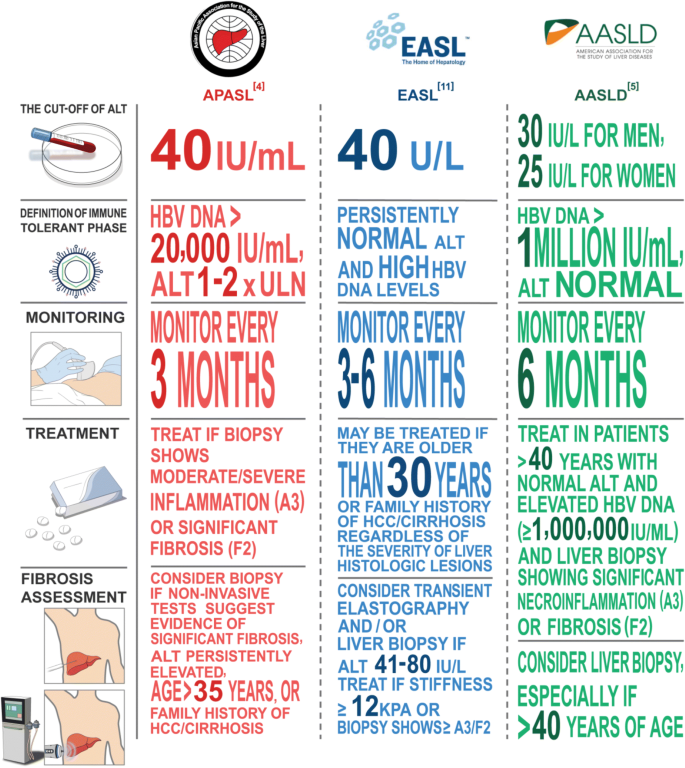
Unresolved Issues Of Immune Tolerance In Chronic Hepatitis B Springerlink

Hbsag And Hbv Dna Levels In The 87 Subjects At M0 M2 And M4 Download Table

Roc Curve Analysis Using Hbsag 900 Iu Ml For Prediction Of Hbv Download Table
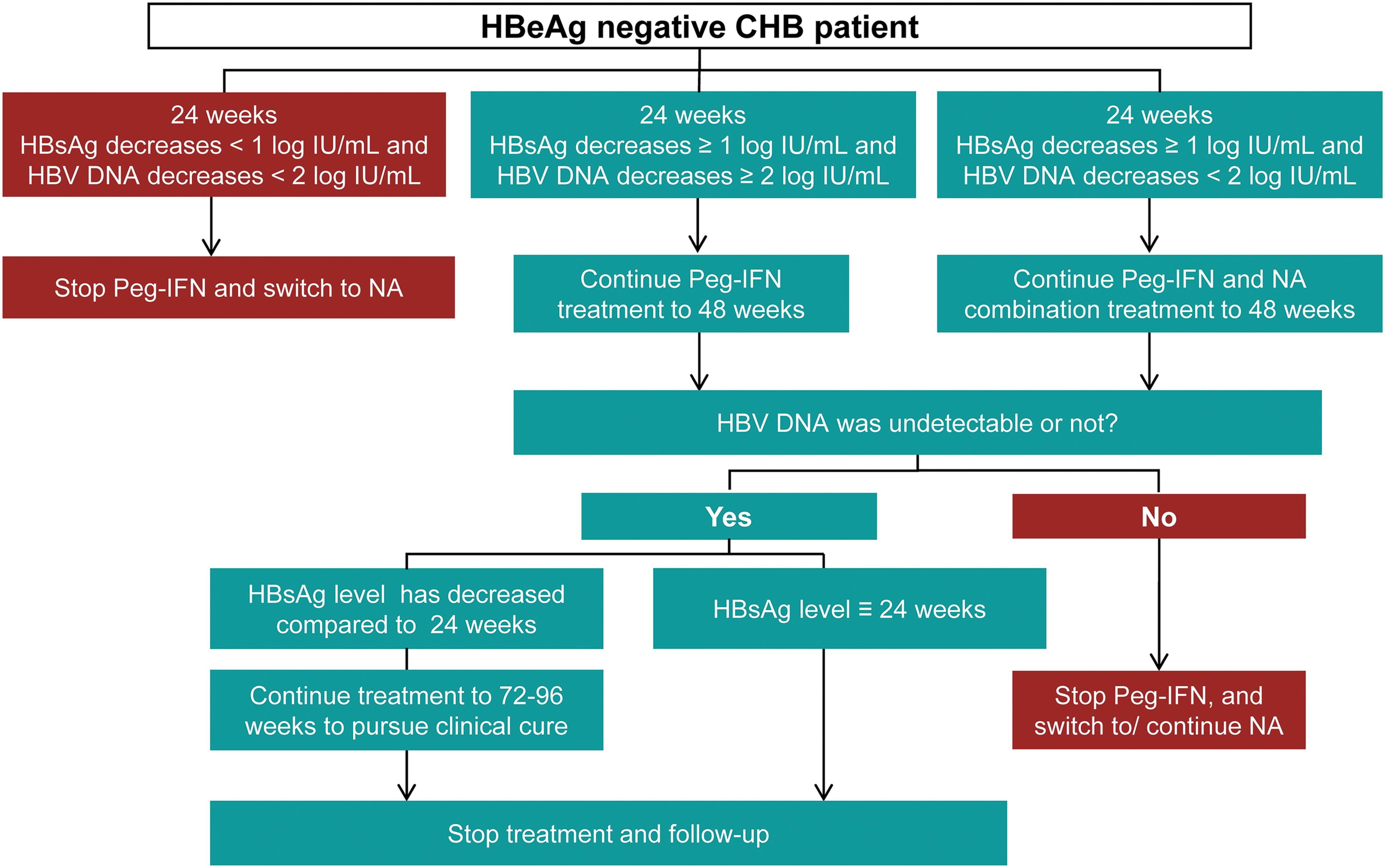
Consensus On Pegylated Interferon Alpha In Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B

Clin Mol Hepatol Clin Mol Hepatol Cmh Clinical And Molecular Hepatology 2287 2728 2287 285x The Korean Association For The Study Of The Liver 10 3350 Cmh 14 3 223 Review Risk Stratification Of Hbv Infection In Asia Pacific Region Kao Jia Horng

Poster Session 3 Hepatitis B Epidemiology And Natural History History 15 Hepatology Wiley Online Library

Tenofovir Prophylaxis For Preventing Mother To Child Hepatitis B Virus Transmission In China A Cost Effectiveness Analysis International Journal Of Infectious Diseases

Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection The Lancet
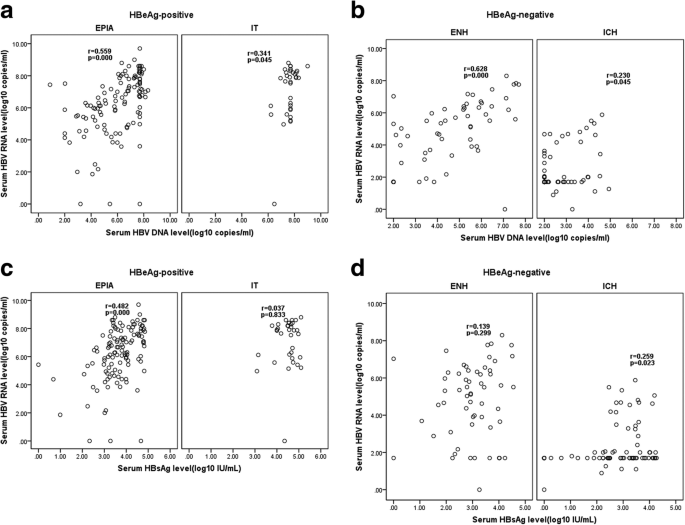
Serum Hbv Rna Quantification Useful For Monitoring Natural History Of Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Bmc Gastroenterology Full Text

Main Baseline Characteristics Of 150 Patients With Hbeag Negative Download Table
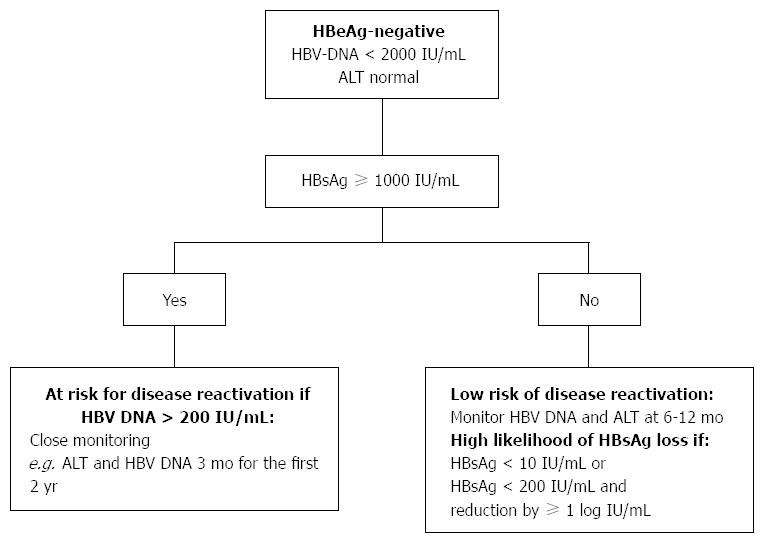
Practical Approach In Hepatitis B E Antigen Negative Individuals To Identify Treatment Candidates
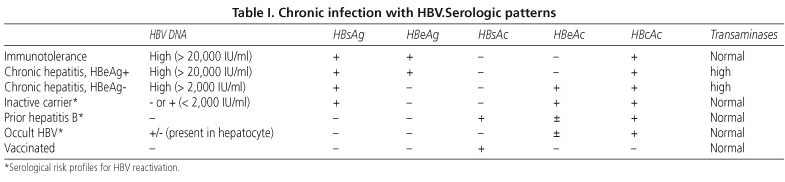
Reactivacion De La Hepatitis B Y Su Impacto Clinico Actual

Hepatitis Monthly Characterization Of Serum Hbv Rna In Patients With Untreated Hbeag Positive And Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Infection

Quantitative Hbv Dna Results For Hbsag Negative Anti Hbc Positive Download Table
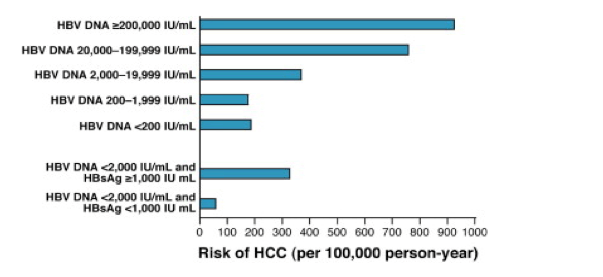
Identifying Hepatitis B Carriers At Low Risk For Hepatocellular Carcinoma Editorial

Quantitative Maternal Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Predicts Maternally Transmitted Hepatitis B Virus Infection Wen 16 Hepatology Wiley Online Library

Viral Hepatitis Cancer Therapy Advisor

Characteristics Of Hepatitis B Core Antibody Level In The Natural History Of Chronic Hepatitis B Jian Wang Discovery Medicine

Association Between Negative Results From Tests For Hbv Dna And Rna And Durability Of Response After Discontinuation Of Nucles T Ide Analogue Therapy Sciencedirect

Hepatitis Monthly Characterization Of Serum Hbv Rna In Patients With Untreated Hbeag Positive And Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
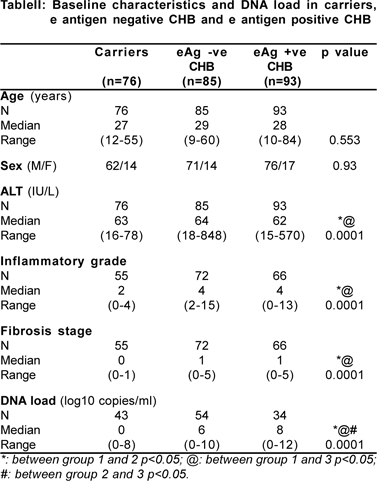
Clinical Relevance Of Hbv Dna Load In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Infection

Inter Assay Analysis Of Hepatitis B Virus Dna Levels Of Reference Sera Download Table
Q Tbn 3aand9gctnczk Zeoncwquzv2jaw2oul3fzjozccljyt0z9wy9fcfvlsjh Usqp Cau

Association Of Hepatitis B E Antigen And Dna Viral Load With Severity Of Liver Dysfunction And In Hospital Outcomes In Hepatitis B Related Liver Cirrhosis Hou Ame Medical Journal

Management Of Chronic Hepatitis B An Overview Of Practice Guidelines For Primary Care Providers American Board Of Family Medicine
Hbv Treatment And Management Hepatic Health
Tim 3 Expression On T Cells Is Correlated With Liver Inflammation Fibrosis And Virological Characteristics In Treatment Naive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients A Cross Sectional Study Gu Annals Of Blood
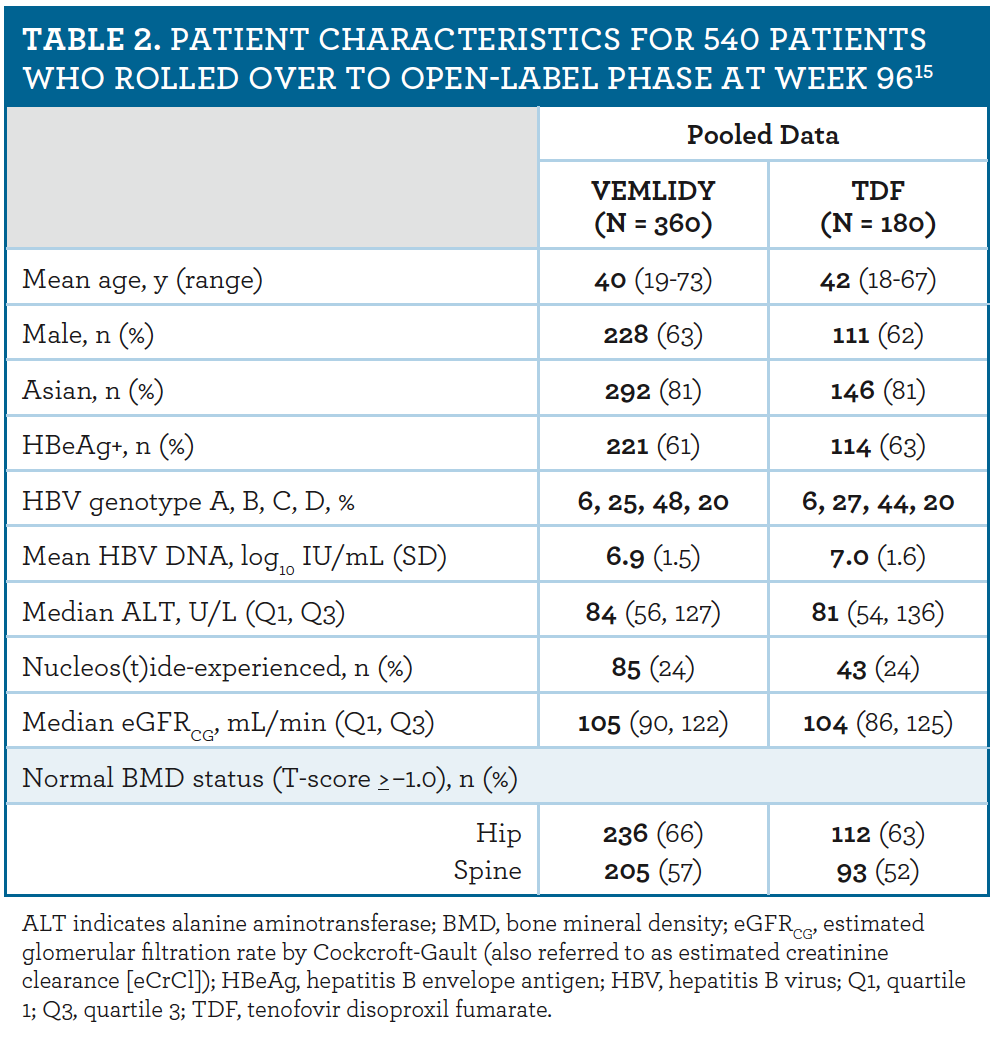
A Pharmacist S Guide To A Once Daily Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
2

Treatment Candidate Selection Based On Clinical Stage Hbeag Hbv Dna Download Table

Rebound Of Hbv Dna After Cessation Of Nucleos Tide Analogues In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With Undetectable Covalently Closed Circular Dna Jhep Reports

Realtime Hbv Viral Load Assay Abbott Molecular
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq Ms8y184mdptf5oviogvpppxvtdt Ocuclileqpmssdb87mw1 Usqp Cau
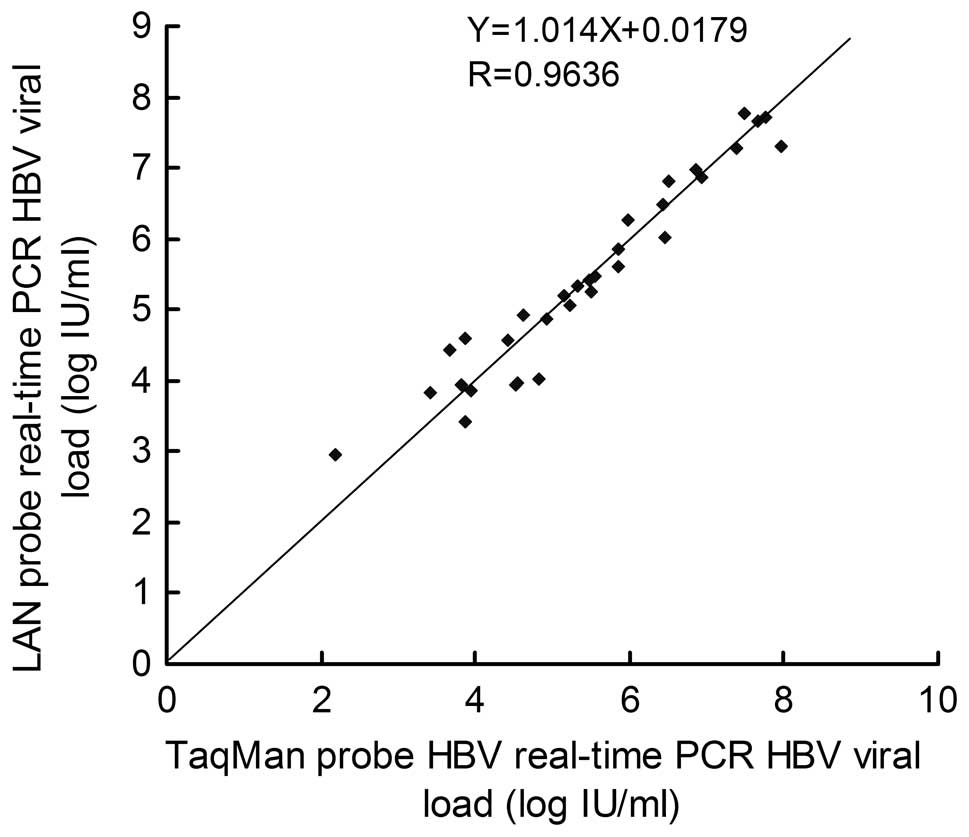
Lna Real Time Pcr Probe Quantification Of Hepatitis B Virus Dna
Diagnosed With Chronic Hepatitis B What Does Your Hbv Dna Test Viral Load Tell You Hepatitis B Foundation

What Is The Best Way To Predict Disease Progression In Patients With Inactive Hbv Aga Journals Blog
The Relationship Between Serum Hepatitis B Virus Dna Level And Liver Histology In Patients With Chronic Hbv Infection
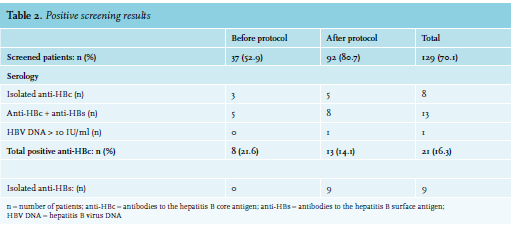
Article Introduction Of Routine Hepatitis B Screening For All Patients Receiving Cancer Treatment Full Text January 19 Njm
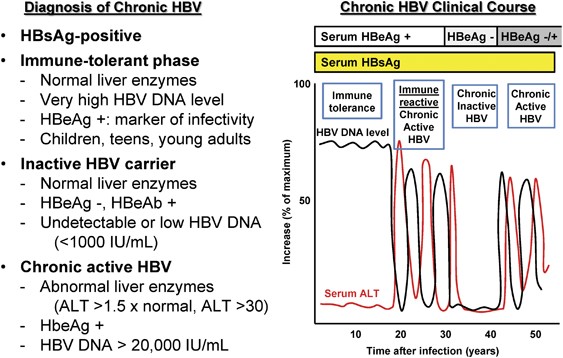
Hepatitis B And C In Pregnancy A Review And Recommendations For Care Journal Of Perinatology
Www Cghjournal Org Article S1542 3565 16 1 Pdf

The New Aptima Hbv Quant Real Time Tma Assay Accurately Quantifies Hepatitis B Virus Dna From Genotypes A To F Journal Of Clinical Microbiology

Full Text Serum Hepatitis B Core Antibody Levels Predict Hbeag Seroconversion In Idr

Comparison Of Different Hepatitis B Guidelines Sethy Pk Goenka Mk Hep B Annual

Clinical Laboratory And Virological Characteristics Of Patients With Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen In Upper Egypt Morsy Kh Ghaliony Ma El Melegy Tt Egypt J Intern Med

Hepatitis B Virus Dna Stability In Plasma Samples Under Short Term Storage At 42 C
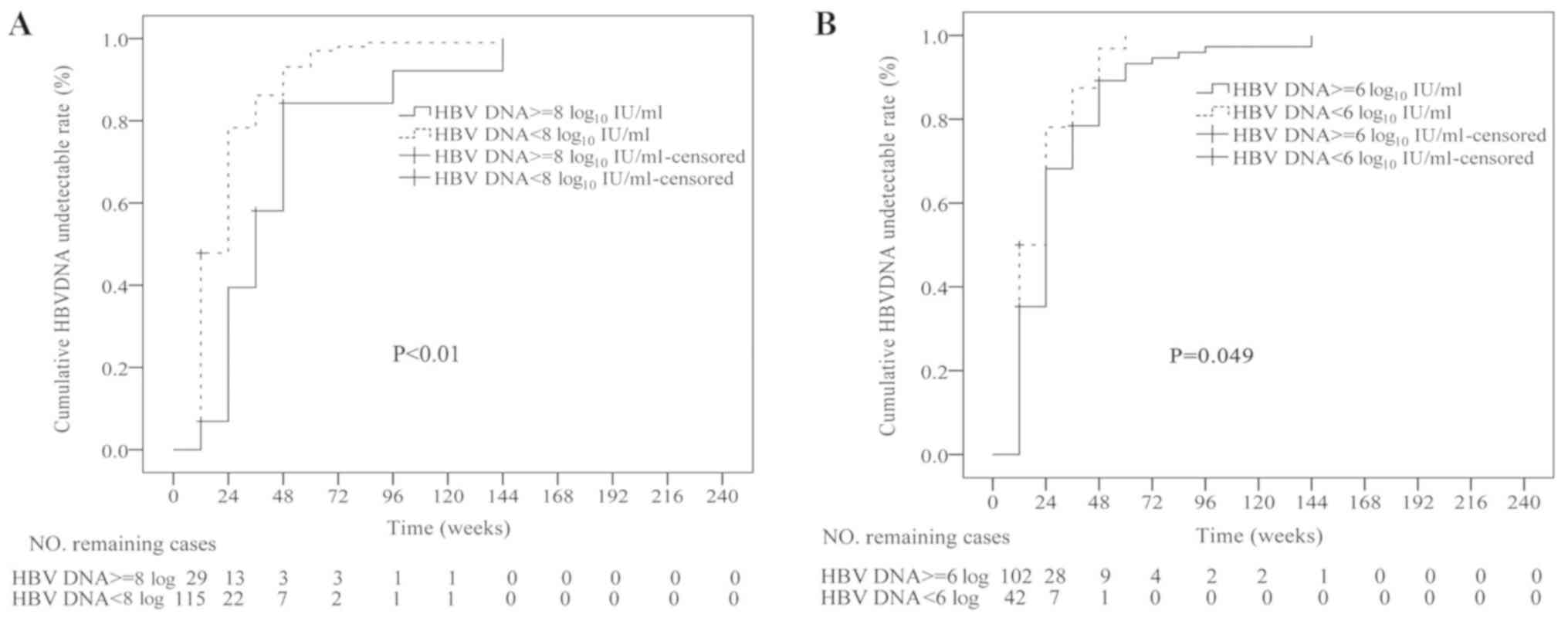
Efficacy Of Long Term Treatment With Tenofovir In Chinese Nucleos T Ide Naive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Regardless Of Baseline Viral Load
The Role Of Hbsag Levels In The Current Management Of Chronic Hbv Infection

Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Correlate With High Serum Hbv Dna Levels In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B A Cross Sectional Study Gupta E Kumar A Choudhary A Kumar M Sarin S K
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmixdydp9zxbvoxpm6gpkob4asxbgucvxco9h 6ujissfkp0ve Usqp Cau

Comparison Of Groups According To Hbv Dna Values Download Table

Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Correlate With High Serum Hbv Dna Levels In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B A Cross Sectional Study Gupta E Kumar A Choudhary A Kumar M Sarin S K
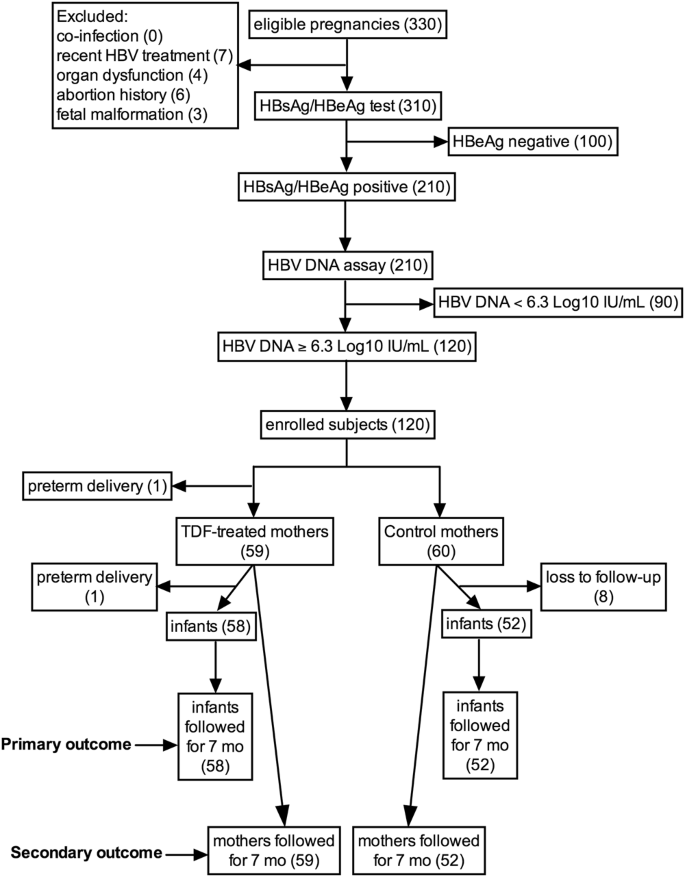
Efficacy Of Tenofovir In Preventing Perinatal Transmission Of Hbv Infection In Pregnant Women With High Viral Loads Scientific Reports
Www Medicine Uci Edu Gisymposium Pdf Pan Pdf

Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Quantification Why And How To Use It In 11 A Core Group Report Sciencedirect

Comparison Of Different Hepatitis B Guidelines Sethy Pk Goenka Mk Hep B Annual
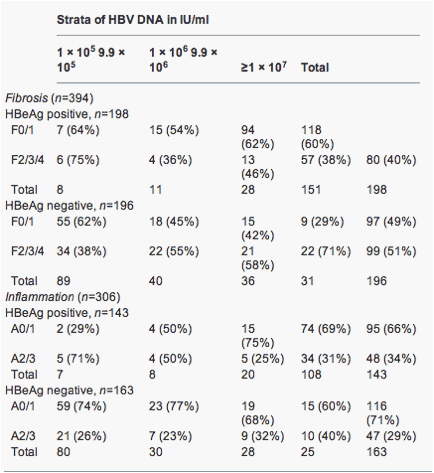
Hbv Viral Load Fibrosis Alt Inflammation Hbeag Hbeag Increasing Hepatitis B Viral Load Is Associated With Risk Of Significant Liver Fibrosis In Hbeag Negative But Not Hbeag Positive Chronic Hepatitis B

Hbv Dna Test In Hindi Hbv Dna Quantitative Test In Hindi Hbv Dna Viral Load Hbv Dna Report Youtube
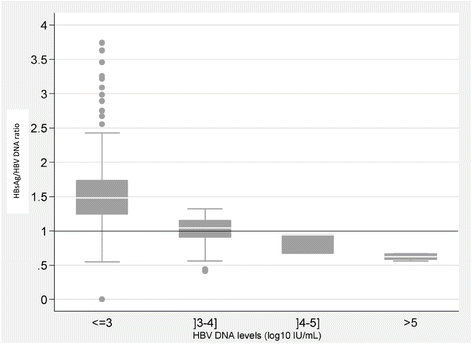
Short Term Spontaneous Fluctuations Of Hbv Dna Levels In A Senegalese Population With Chronic Hepatitis B Bmc Infectious Diseases Full Text
Www Cghjournal Org Article S1542 3565 19 6 Pdf

Current Treatment Of Hepatitis B Virus Infections Med Virology 15
Clinical And Histopathological Features Of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infected Patients With High Hbv Dna Viral Load And Normal Alanine Aminotransferase Level A Multicentre Based Study In China

Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes Precore Mutations And Basal Core Promoter Mutations In Hbv Infected Chinese Patients With Persistently Normal Alanine Aminotransferase And Low Serum Hbv Dna Levels

Quantitative Nucleic Acid Amplification Methods And Their Implications In Clinical Virology
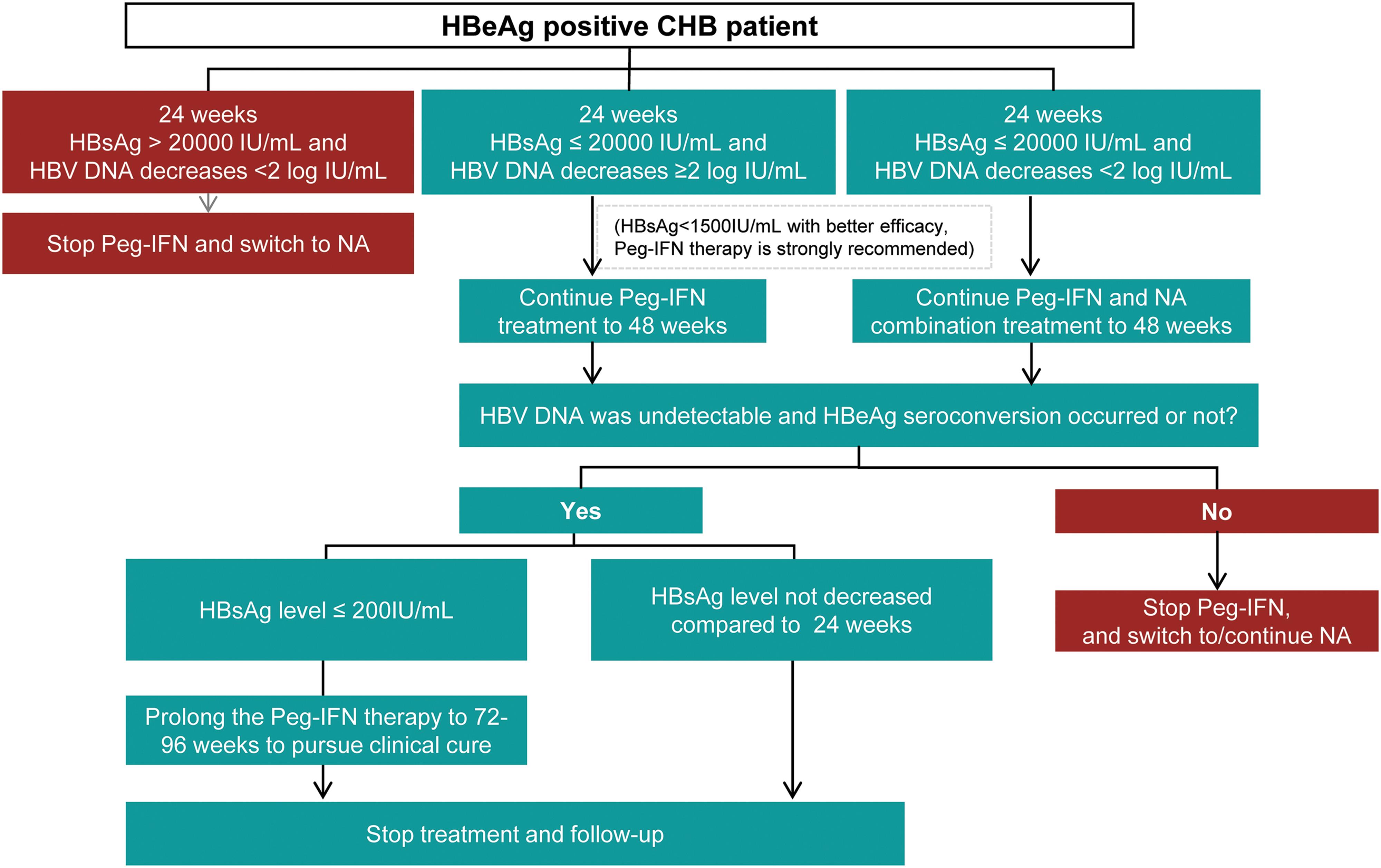
Consensus On Pegylated Interferon Alpha In Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B
Q Tbn 3aand9gctnczk Zeoncwquzv2jaw2oul3fzjozccljyt0z9wy9fcfvlsjh Usqp Cau

Experience With Hepatitis B Viral Load Testing In Jharkhand
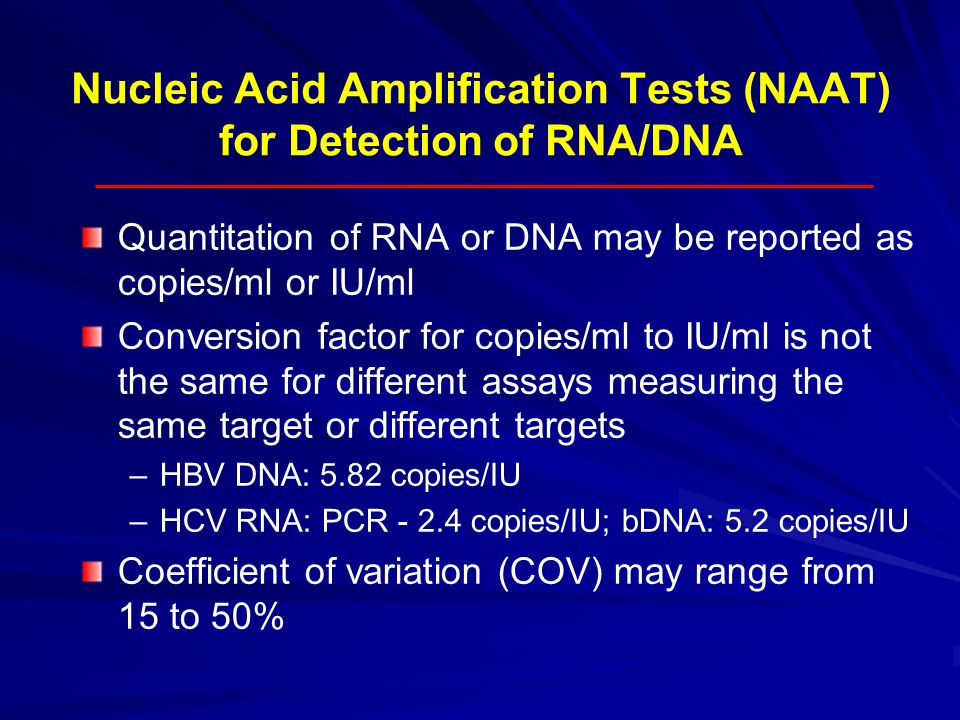
Laboratory Diagnostics In Hepatitis Ppt Video Online Download
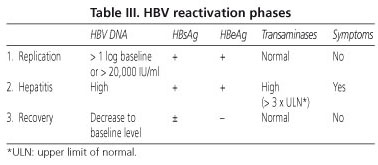
Reactivacion De La Hepatitis B Y Su Impacto Clinico Actual

High Levels Of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Increase Risk Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Patients With Low Hbv Load Gastroenterology

Hepatitis B Infection And Mother To Child Transmission In Haiphong Vietnam A Cohort Study With Implications For Interventions
Http Www Gastrojournal Org Article S0016 5085 10 8 Pdf

Hepatitis B Viral Load In Diagnosing Different Clinical Stages Of Chronic Hepatitis B In A Tertiary Care Hospital In North Kerala Balakrishnan Sm Moorkoth Ap Sarada Devi K L Philomina B Lilabi
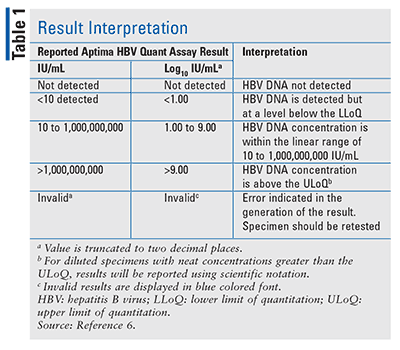
Aptima Hbv Quant Assay

What Is The Best Way To Predict Disease Progression In Patients With Inactive Hbv Aga Journals Blog
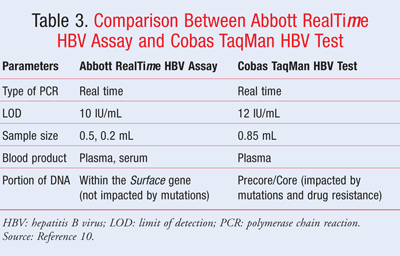
Real Time Hepatitis B Virus Assay
Www Hepb Org Assets Uploads Hbf Pedspaper Nov 09 Pdf
Plos One Ultrasensitive Detection Of Serum Hepatitis B Virus By Coupling Ultrafiltration Dna Extraction With Real Time Pcr
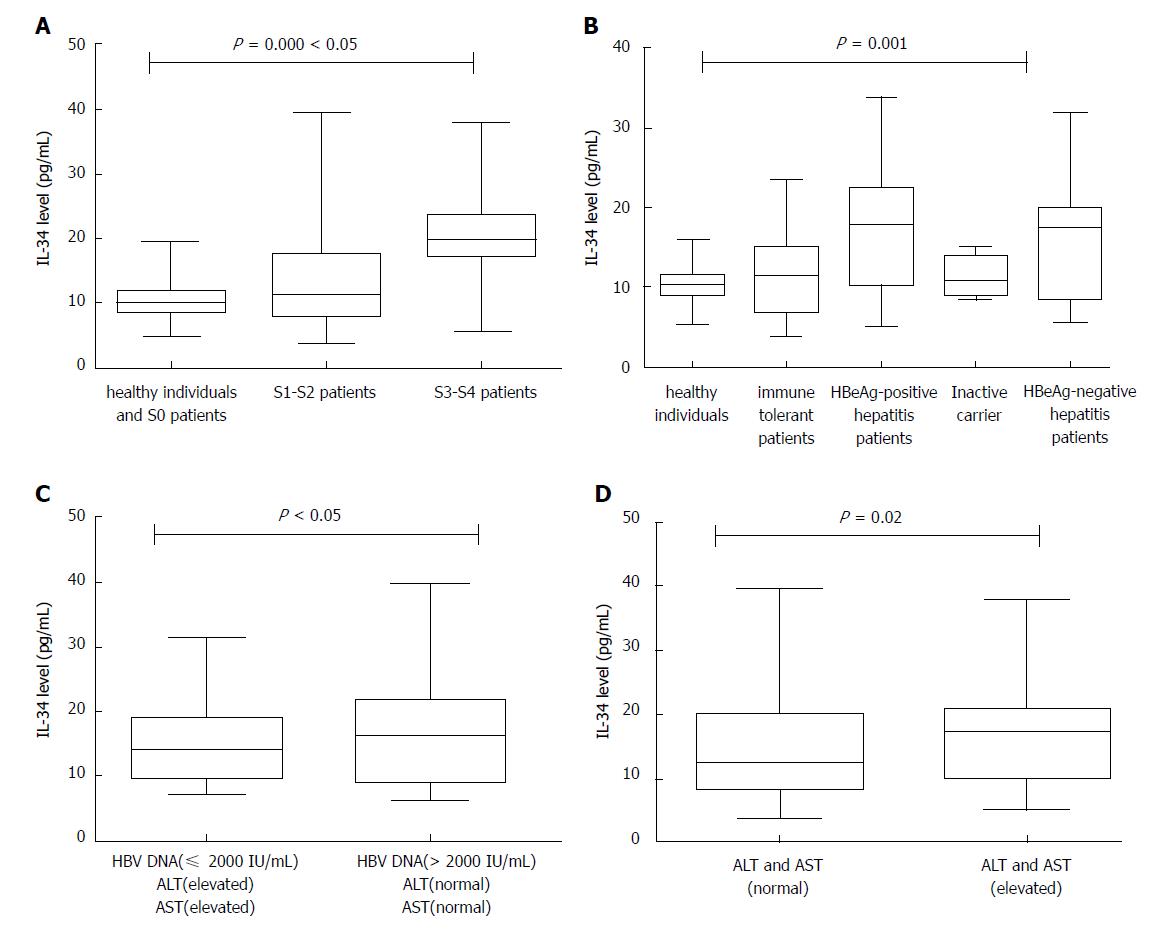
Serum Interleukin 34 Level Can Be An Indicator Of Liver Fibrosis In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
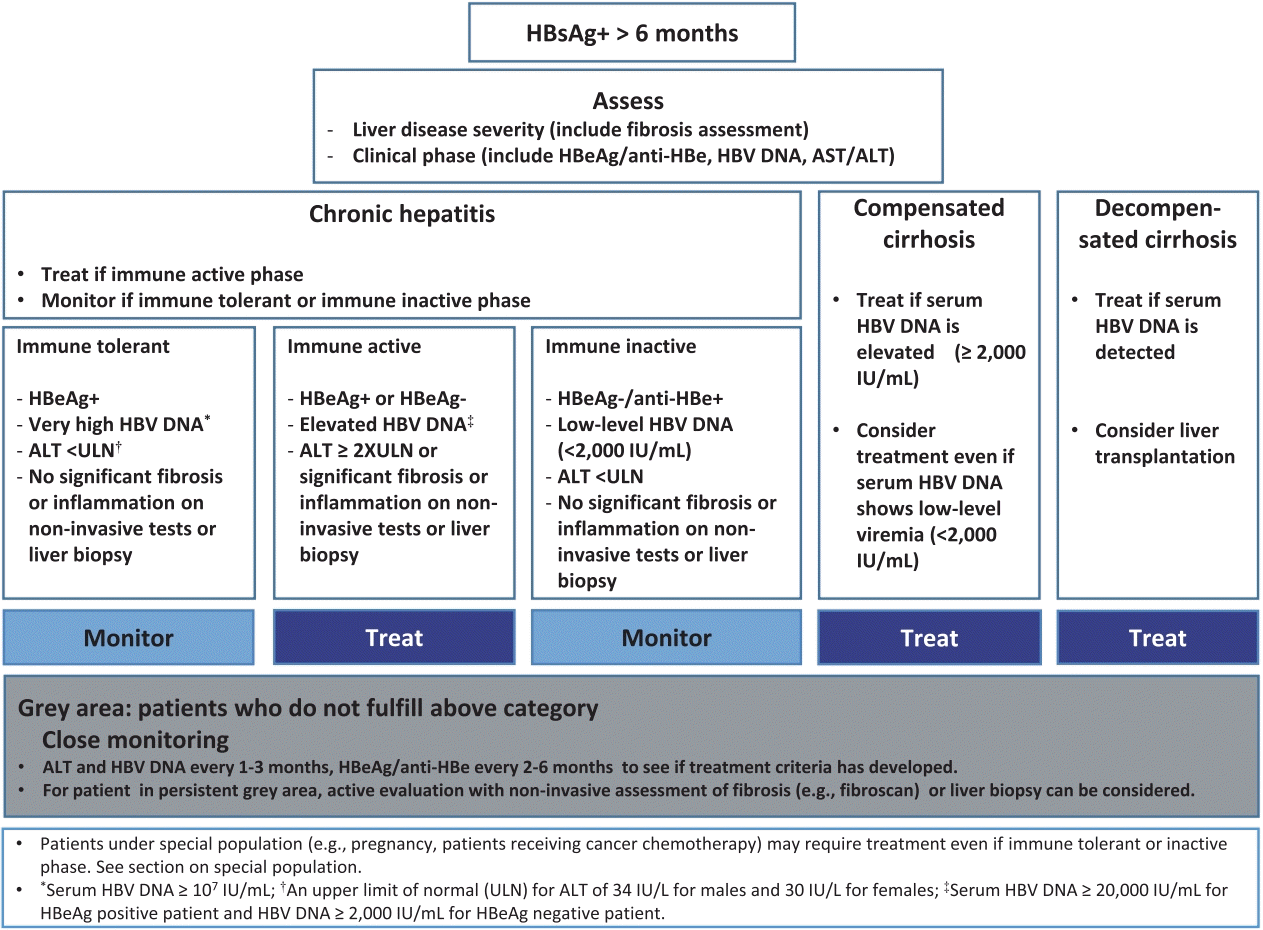
Kasl Clinical Practice Guidelines For Management Of Chronic Hepatitis B

Add On Pegylated Interferon Augments Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Clearance Vs Continuous Nucleos T Ide Analog Monotherapy In Chinese Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B And Hepatitis B Surface Antigen 1500 Iu Ml An Observational Study

Serological And Virological Markers Of Nigerian Patients With Hepatitis B Infection Lesi O A Audu R A Okwuraiwe A P Adeleye O O Ige F A Iwuorah J C Niger J Clin Pract

Jsh Guidelines For The Management Of Hepatitis B Virus Infection 14 Hepatology Research Wiley Online Library
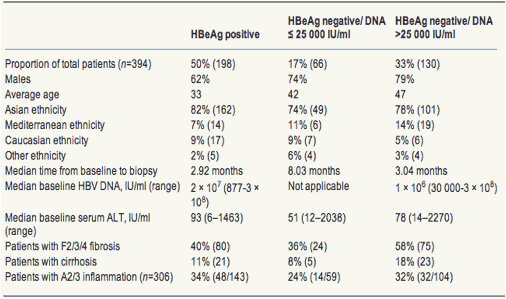
Hbv Viral Load Fibrosis Alt Inflammation Hbeag Hbeag Increasing Hepatitis B Viral Load Is Associated With Risk Of Significant Liver Fibrosis In Hbeag Negative But Not Hbeag Positive Chronic Hepatitis B



